Answer:

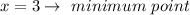
Explanation:
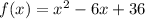
The derivative is:
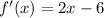
To calculate the max/min point of the function, we use the first derivative and put it equal to zero (if needed)
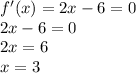
To check whether this point is max or min, we substitute the value of x in the second derivative of the function. If the answer is positive, the value is minimum. If the answer is negative, the value is minimum.
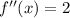
The second derivative is positive, hence
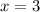 is minimum.
is minimum.