Answer:
19.56 kg/s
Step-by-step explanation:
In the given problem, we have:
The temperature
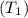 and pressure into the system are 300 K and 1 bar respectively. The outlet temperature
and pressure into the system are 300 K and 1 bar respectively. The outlet temperature
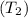 and pressure
and pressure
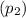 are 500 K and 5 bar respectively. The heat transfer rate
are 500 K and 5 bar respectively. The heat transfer rate
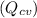 is 30 kW and the power input
is 30 kW and the power input
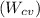 is 4000 kW.
is 4000 kW.
If we consider the energy balance equation and neglect both kinetic energy and potential energy, we have:
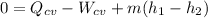
Thus, the mass flow rate (m) is:
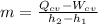
If we use the thermodynamic table for air:
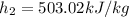 ,
,
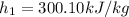 ,
,
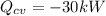 , and
, and
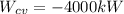 . Therefore:
. Therefore:
m = [-30-(-4000)]/[503.02-300.10] = 3970/202.92 = 19.56 kg/s