Answer:
2.73 is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of
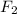 gas at 840 degree Celsius.
gas at 840 degree Celsius.
Step-by-step explanation:
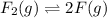
Initial
0.600 atm 0
Equilibrium
(0.600 atm - p) 2p
Total pressure at equilibrium = P = 0.984 atm
P= 0.600 atm - p)+2p=0.984 atm
p = 0.384 atm
Partial pressure of the
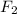 gas ,
gas ,
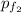 = (0.600 atm - 0.384 atm)=0.216 atm
= (0.600 atm - 0.384 atm)=0.216 atm
Partial pressure of the
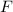 gas,
gas,
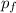 = 2(0.384 atm)=0.768 atm
= 2(0.384 atm)=0.768 atm
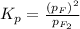
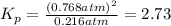
2.73 is the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of
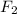 gas at 840 degree Celsius.
gas at 840 degree Celsius.