Answer:
Angular velocity is same as frequency of oscillation in this case.
ω =
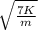 x
x
![[(L^(2))/(mK)]^(3/14)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/mgop0tg5rrkfx02itaa1xj0tp2b42crpuh.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
- write the equation F(r) = -K
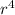 with angular momentum L
with angular momentum L
- Get the necessary centripetal acceleration with radius r₀ and make r₀ the subject.
- Write the energy of the orbit in relative to r = 0, and solve for "E".
- Find the second derivative of effective potential to calculate the frequency of small radial oscillations. This is the effective spring constant.
- Solve for effective potential
- ω =
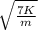 x
x
![[(L^(2))/(mK)]^(3/14)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/mgop0tg5rrkfx02itaa1xj0tp2b42crpuh.png)