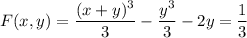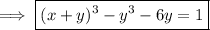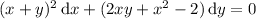
Suppose the ODE has a solution of the form
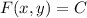 , with total differential
, with total differential
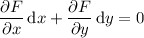
This ODE is exact if the mixed partial derivatives are equal, i.e.
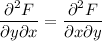
We have
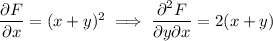
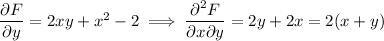
so the ODE is indeed exact.
Integrating both sides of
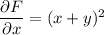
with respect to
 gives
gives
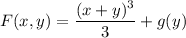
Differentiating both sides with respect to
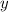 gives
gives
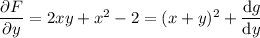
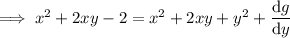
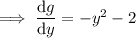
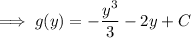
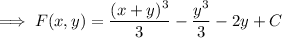
so the general solution to the ODE is
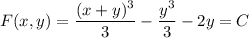
Given that
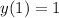 , we find
, we find
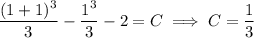
so that the solution to the IVP is