Answer:
Speed of electron when their separation increased by a factor of 4.10 is 9.41 x 10⁵ m/s .
Step-by-step explanation:
The electric potential energy is given by the relation :
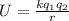
Here q₁ and q₂ are the two charge particles and r is the distance between them and k is electric constant.
In this case, there are two electrons which are separated by the distance 4.32 x 10⁻¹⁰ m.
Let e be the electron charge and r₁ be the distance between them. Then, the initial electric potential energy is :
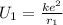
Now, the distance between the electrons increases by the factor of 4.10. Let r₂ be the new distance between them i.e. r₂ = 4.10 r₁.
Thus, the new electric potential energy is :
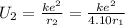
Applying law of conservation of energy :
ΔU = ΔK
Here ΔU is change in electric potential energy and ΔK is change in kinetic energy.
( U₁ - U₂ ) = ( K₂ - K₁ )
Here K₂ and K₁ are initial and final kinetic energy of electron.
Since, the electron initially is at rest, so its initial kinetic energy is zero. Thus, the above equation becomes:
K₂ = U₁ - U₂
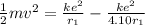
Here m and v are the mass and final speed of electron respectively.
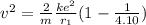
Substitute 9.1 x 10⁻³¹ kg for m, 9 x 10⁹ N m² C⁻² for k, 1.6 x 10⁻¹⁹ C for e and 4.32 x 10⁻¹⁰ m for r₁ in the above equation.
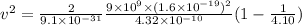
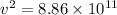
v = 9.41 x 10⁵ m/s