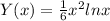Answer:
Therefore the particular solution of the given differential equation is
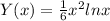
Explanation:
The given ordinary differential equation is
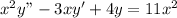
If y₁(x) =x² is a solution of ODE then it will be satisfy the ODE
y₁'(x)= 2x and y₁"(x)=2
Putting the value of y₁'(x) and y₁"(x) in x²y"-3xy'+4y=0 we get
x².2-3x.2x+4x²= 2x²-6x²+4x²=0
Therefore y₁(x) is a solution of the given differential equation.
Again,
y₂(x) =(x²ln x ) is a solution of ODE then it will be satisfy the ODE.
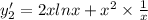
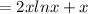
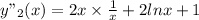 = 3+2 ln x
= 3+2 ln x
Putting the value of y₂'(x) and y₂"(x) in x²y"-3xy'+4y=0 we get
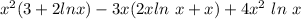 =0
=0
Therefore y₂(x) is a solution of the given differential equation.
The wronskian of y₁(x) and y₂(x) is
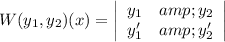
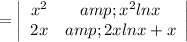
=x²(2x ln x+x)-x²ln x(2x)
=2x³ ln x +x³ - 2x³ln x
=x³≠0
Here
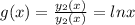
The particular solution is
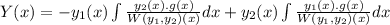
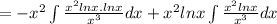
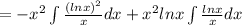
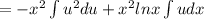 Let ln x =u
Let ln x =u
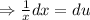
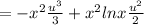
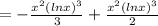
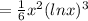
Therefore the particular solution of the given differential equation is