Answer:
The average current I supplied to the cars motor is 0.225 Amperes.
Step-by-step explanation:
The mass of the toy car is given as, m = 0.6 kg
The toy car operates at a steady speed of, v = 3.43 m/s.
It achieves the steady speed after a time, t = 5.69 seconds.
The total kinetic energy of the car is given by,
E =
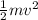
= 0.5 × 0.6 ×
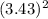
= 3.53 Joules
Since the efficiency of the motor is 30.6% = 0.306
The electrical energy equivalent is supplied to motor =
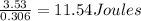 .
.
The electrical energy is given by P × t = I × V × t = 11.54 Joules
P is the electric power where P = I × V where V is the voltage of the cell and is the average current, I.
Therefore we can write I × 9 × 5.69 = 11.54 Joules.
So the average current I =
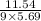 = 0.225 Amperes.
= 0.225 Amperes.