Answer:
B) and D)
Step-by-step explanation:
According to the law of conservation of energy, the initial elastic potential energy stored in the compressed spring is transformed into kinetic energy of motion of the dart as it is released, and then into gravitational potential energy at the highest position of the dart.
So, we can write that the initial elastic potential energy of the compressed spring is equal to the kinetic energy with which the dart leaves the spring:
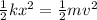
where the term on the left is the elastic potential energy while the term on the right is the kinetic energy, and where
k is the spring constant
x is the compression of the spring
m is the mass of the dart
v is its initial speed
Re-arranging the equation making the speed the subject, we get
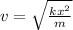 (1)
(1)
So, this is the initial speed with which the dart leaves the spring.
Also, we can write that the initial elastic potential energy of the compressed spring is equal to the final gravitational potential energy when the dart is at its highest position:
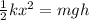
where the term on the left is the elastic potential energy while the term on the right is the gravitational potential energy, and where:
k is the spring constant
x is the compression of the spring
m is the mass of the dart
g is the acceleration due to gravity
h is the maximum height reached by the dart
We can re-arrange the equation making h the subject:
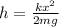 (2)
(2)
So, this is the maximum height reached by the dart.
Now we can analyze each statement:
A) The heavy dart goes higher than the light dart. --> FALSE. As we see from eq(2), the maximum height is inversely proportional to the mass of the dart, so the light dart goes higher than the heavy dart.
B) The light dart goes higher than the heavy dart. --> TRUE, as stated in A).
C) Both darts reach the same maximum height. --> FALSE, as stated for A) and B).
D) At the maximum height, both darts have the same gravitational potential energy. --> TRUE. In fact, their gravitational potential energy is equal to the initial elastic potential energy, and since the spring was initially compressed by the same amount, the elastic potential energy was the same.
E) Both darts began moving upward with the same initial speed. --> FALSE. From eq.(1), we see that the initial speed depends on the mass, therefore their initial speeds are different.