This is an incomplete question, here is a complete question.
Suppose a 500 mL flask is filled with 0.30 mol of I₂ and 0.60 mol of HI . The following reaction becomes possible:
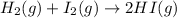
The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.282 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H₂. Round your answer to one decimal place.
Answer : The equilibrium molarity of H₂ is, 0.2 M
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the concentration of
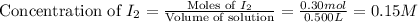
and,
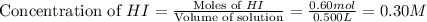
Now we have to calculate the equilibrium molarity of H₂.
The given chemical reaction is:
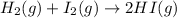
Initial conc. 0 0.15 0.30
At eqm. x (0.15+x) (0.30-2x)
The expression for equilibrium constant is:
![K=([HI]^2)/([H_2][I_2])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/zigyl7hppamwc4ms5fibucq0wyyf6znfd1.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get:
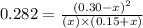
x = 0.174 M and x = 0.721 M
We are neglecting the value of x = 0.721 because the equilibrium concentration can not be more than initial concentration.
Thus, the value of x = 0.174 M ≈ 0.2 M
The equilibrium molarity of H₂ = x = 0.2 M