Answer:
Therefore the equilibrium constant
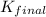 is 9.35× 10²⁵
is 9.35× 10²⁵
Step-by-step explanation:
Equilibrium constant:
Equilibrium constant is used to find out the ratio of the concentration of the product to that of reactant.
xA+yB→zC
The equilibrium constant K,
![k=([C]^z)/([A]^x[B]^y)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/ak1f2aw3n132nyb174wco13gvwsqtjhbpg.png)
Here [A] is equilibrium concentration of A
[B] is equilibrium concentration of B
[C] is equilibrium concentration of C.
1.
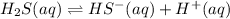
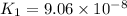
![K_1=([HS^-][H^+])/([H_2S])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/8rdc4m7a6v9np4gnjlqwxez1ydkk0lw6jp.png)
2.
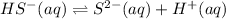
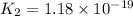
![K_2=([S^(2-)][H^+])/([HS^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/1y8ve8jkhys9x5p6zeh90h50veo4th07a3.png)
3.
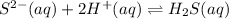
![K_3=([H_2S])/([S^(2-)][H^+]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/sk4s5kn1zoctcuvlo17f52pghcy76q68eb.png)
Therefore,
![k_1k_2=([HS^-][H^+])/([H_2S])([S^(2-)][H^+])/([HS^-])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/oj13cahuw0dwo2aq9iikkpy1wg704mcr4h.png)
![\Rightarrow k_1k_2=([S^(2-)][H^+]^2)/([H_2S])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/vvfhvixu0f4iydi8v51xscj7gygadnw48q.png)
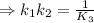
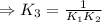
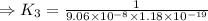
⇒K₃=9.35× 10²⁵
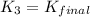
Therefore the equilibrium constant
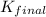 is 9.35× 10²⁵
is 9.35× 10²⁵