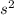Answer:
The angular acceleration required is 0.1765 rad/
Step-by-step explanation:
The radius of the bicycle wheel has a radius of 0.42 m.
The acceleration is for time, t = 6.8 seconds.
Initial angular velocity is given as
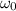 = 5.5 rad/s
= 5.5 rad/s
Final angular velocity is given as
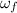 = 6.7 rad/s
= 6.7 rad/s
Therefore from the formula for angular speed we get
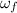 =
=
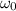 + (
+ (
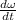
 t), where t is the time in seconds.
t), where t is the time in seconds.
Therefore we get
6.7 = 5.5 + (6.8 ×
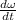 )
)
Therefore we get the angular acceleration,
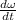 =
=
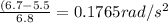
The angular acceleration required is 0.1765 rad/