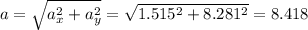1)
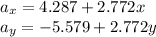
2) 8.418
Step-by-step explanation:
1)
The two components of the velocity field in x and y for the field in this problem are:
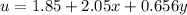
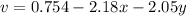
The x-component and y-component of the acceleration field can be found using the following equations:
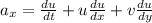
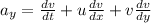
The derivatives in this problem are:
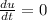
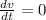
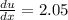
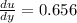
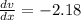
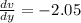
Substituting, we find:
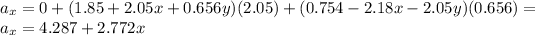
And
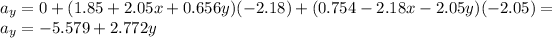
2)
In this part of the problem, we want to find the acceleration at the point
(x,y) = (-1,5)
So we have
x = -1
y = 5
First of all, we substitute these values of x and y into the expression for the components of the acceleration field:
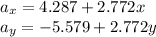
And so we find:
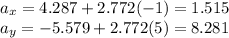
And finally, we find the magnitude of the acceleration simply by applying Pythagorean's theorem: