Answer: The activation energy of the reaction is 113.8 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate activation energy of the reaction, we use Arrhenius equation, which is:
![\ln((K_(258^oC))/(K_(195^oC)))=(E_a)/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/1dbgnk02dobzbv35ujng8q6cn5mevok1h7.png)
where,
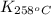 = equilibrium constant at 258°C =
= equilibrium constant at 258°C =
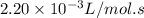
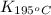 = equilibrium constant at 195°C =
= equilibrium constant at 195°C =
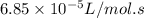
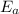 = Activation energy of the reaction = ?
= Activation energy of the reaction = ?
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
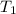 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
![195^oC=[195+273]K=468K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hc3cnfsmfq2ardcpxdf4p395gqm7pty8s1.png)
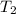 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
![258^oC=[258+273]K=531K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/taiwzdyg0eei7oe0p31mjxcakozyzk1q04.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((2.20* 10^(-3))/(6.85* 10^(-5)))=(E_a)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(468)-(1)/(531)]\\\\E_a=113780J/mol=113.8kJ/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qz3yive2prx2fzzybe1b8m0jsssxeqlnw9.png)
Hence, the activation energy of the reaction is 113.8 kJ/mol