Answer: The activation energy of the reaction is 124.6 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate activation energy of the reaction, we use Arrhenius equation, which is:
![\ln((K_(79^oC))/(K_(26^oC)))=(E_a)/(R)[(1)/(T_1)-(1)/(T_2)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/g2l5isd73kj8tzf4zb9o5u90k5yc6t4ur1.png)
where,
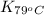 = equilibrium constant at 79°C =
= equilibrium constant at 79°C =
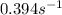
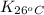 = equilibrium constant at 26°C =
= equilibrium constant at 26°C =
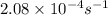
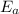 = Activation energy of the reaction = ?
= Activation energy of the reaction = ?
R = Gas constant = 8.314 J/mol K
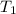 = initial temperature =
= initial temperature =
![26^oC=[26+273]K=299K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/uphu7hpf02nr3bigmkzlpi1fufydfmq2y5.png)
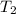 = final temperature =
= final temperature =
![79^oC=[79+273]K=352K](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/8xlp8kw151lhccbeha6otgvsq3t72q0tyz.png)
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![\ln((0.394)/(2.08* 10^(-4)))=(E_a)/(8.314J/mol.K)[(1)/(299)-(1)/(352)]\\\\E_a=124595J/mol=124.6kJ/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/jru246f3pnmrg2r4gf80nd3ygnkjf4r4zu.png)
Hence, the activation energy of the reaction is 124.6 kJ/mol