Answer:
76% probability that a randomly selected customer buys either baby formula or diaper
Explanation
We solve this problem building the Venn's diagram of these probabilities.
There are two events, events B and D.
We have that:
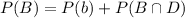
In which P(b) is the probability of only b and
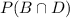 is the probability of both B and D.
is the probability of both B and D.
By the same logic, we have that:
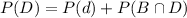
P(B)=0.62, P(D)=0.52 and P(B∩D)=0.38.
So
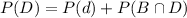
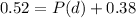
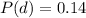
And
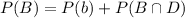
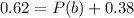
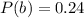
What is the probability that a randomly selected customer buys either baby formula or diaper?
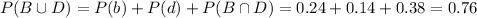
76% probability that a randomly selected customer buys either baby formula or diaper