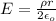Answer:
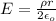
option D
Step-by-step explanation:
The correct choice of Gaussian surface would be (D) a finite closed cylinder whose axis coincides with the axis of the rod and whose cross-section has a radius of
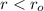 . This is because the charged cylinder is of infinite length and hence there won't be any electric flux coming out of the top and bottom flat surfaces.
. This is because the charged cylinder is of infinite length and hence there won't be any electric flux coming out of the top and bottom flat surfaces.
Now, to find out the magnitude of the electric field
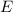 , we shall have to apply Gauss's law,
, we shall have to apply Gauss's law,
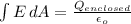
or,
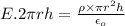 (
(
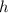 being the height of the Gaussian cylinder)
being the height of the Gaussian cylinder)
or,