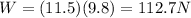1) 11.5 kg
2) 11.5 kg
3) 112.7 N
Step-by-step explanation:
1)
The relationship between the mass of an object and its weight is given by the relationship:
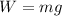
where:
W is the weight
m is the mass of the object
g is the acceleration due to gravity (the strength of the gravitational field at the location of the object)
In this problem, the object is on Mars.
Its weight is:
W = 42.7 N
While the acceleration due to gravity is:
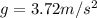
Therefore, we can re-arrange the equation to find the mass of the rover:
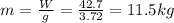
2)
Here we want to find the mass of the rover on Earth.
We have to identify the main difference between mass and weight:
- The mass of an object is an intrinsec property of the object, and it describes the "amount of matter" contained in the object
- The weight of an object is the force of gravity acting on the object itself
From the definitions above, it is clear that:
- The mass of an object is independent from its location, therefore it does not change if the object moves to another planet
- The weight of an object depends on its location, as it depends on the value of
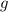 , the acceleration due to gravity
, the acceleration due to gravity
Therefore, the mass of the rover on the Earth is the same as the mass of the rover on Mars:
m = 11.5 kg
3)
The weight of an object, as stated before, is the force of gravity acting on the object, and it is given by
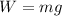
where
m is the mass of the object
g is the acceleration due to gravity
On the surface of the Earth, the value of the acceleration due to gravity is
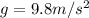
While the mass of the rover is
m = 11.5 kg
Therefore, the weight of the rover on Earth is