Answer:
Work done by the gas during initial expansion is 564 J.
Step-by-step explanation:
Given :
Number of moles, n = 0.200
Initial pressure, P = 2.40 x 10⁵ Pa
Initial temperature, T = 340 K
According to the problem, it consider oxygen as an ideal gas. Hence, ideal gas equation can be applied on oxygen. Thus,
PV = nRT
Here P is pressure, V is volume, n is number of mole, R is universal gas constant and T is temperature.
V = (nRT)/P
Substitute the suitable values in the above equation.
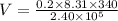
V = 2.35 x 10⁻³ m³
It is the initial volume of the gas.
According to the problem, the gas expands isobarically i.e. its pressure remains same throughout the process.
But its volume changes to twice of initial volume i.e.
V₁ = 2V
Work done during isobaric process is given by the equation :
W = P ( V₁ - V )
Substitute the suitable values in the above equation.
W = 2.40 x 10⁵ x ( 2 x 2.35 x 10⁻³ - 2.35 x 10⁻³ )
W = 564 J