Answer:
The value of ΔH when 21.9 grams of hydrogen gas reacts with an excess of oxygen gas is 2,647.71 kilo Joules.
Step-by-step explanation:
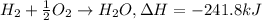
Mass of hydrogen gas = 21.9 g
Moles of hydrogen gas =
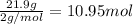
When 1 mole of hydrogen gas reacts with an excess oxygen gas it gives 241.8 kJ of heat.
Then 10.95 moles hydrogen gas will give :
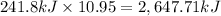
The value of ΔH when 21.9 grams of hydrogen gas reacts with an excess of oxygen gas is 2,647.71 kilo Joules.