Answer:
a. E = 0.
b.
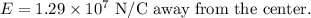
c. E = 0.
Step-by-step explanation:
We will apply Gauss' Law to find the electric field at the given location. We will draw an imaginary spherical shell with radius 'r'. The electric field through the surface of the shell will be equal to the total charge enclosed by this imaginary surface.
Gauss' Law:
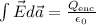
a. r = 2.5 cm (inside the smaller shell)
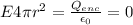
Since there is no charge inside the spheres, the electric field in that region is equal to zero.
b. r = 7.5 cm (between the shells)
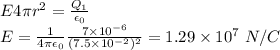
Since the charge of the inner surface is positive, the electric field is away from the center.
c. r = 12.5 cm (outside the shells)
Since the total charge of two shells are equal to zero, the electric field outside the shells is zero as well.