Answer : The expression that gives the equilibrium concentration of N₂O in terms of K₁, K⁻¹ and the equilibrium concentrations of N₂ and O₂ is:
![[N_2O]=(K^(-1))/(K_1)* [N_2][O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/46ue9qy19fplcjcqqu2gelilpecsrnj8mc.png)
Explanation :
As we are given that:
The rate of reaction in forward direction =
![R_f=K_1* [N_2O]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/msmuwo4l2j30ius1ltm5gxtuctteatd7pz.png)
The rate of reaction in backward direction =
![R_b=K^(-1)* [N_2][O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/f7jxrlaspgunilrq3gq63hff5qi5rtpg1h.png)
As we know that at equilibrium, rate of forward reaction is equal to the rate of backward reaction.
So,
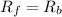
![K_1* [N_2O]=K^(-1)* [N_2][O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/dp3xtt6blublaa3j2ohn307v43q4m2jd6t.png)
The expression that gives the equilibrium concentration of N₂O in terms of K₁, K⁻¹ and the equilibrium concentrations of N₂ and O₂ is:
![[N_2O]=(K^(-1))/(K_1)* [N_2][O_2]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/46ue9qy19fplcjcqqu2gelilpecsrnj8mc.png)