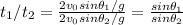Answer:
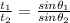
Step-by-step explanation:
The vertical component of the initial velocities are
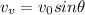
If we ignore air resistance, and let g = -9.81 m/s2. The the time it takes for the projectiles to travel, vertically speaking, can be calculated in the following motion equation
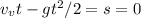
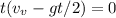
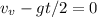
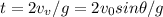
So the ratio of the times of the flights is