Answer:
185.95 μsec
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that:
Sine wave =
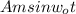
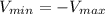
Sinusodial signal
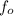 = 50 kHz =
= 50 kHz =
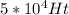
Rise time is said to be defined as the time needed for a pulse to rise from 10% - 90% of maximum rate.
∴
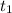 = 10% = 0.1 Am
= 10% = 0.1 Am
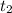 =90% = 0.9 Am
=90% = 0.9 Am
Using sine wave for
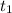 ; we have:
; we have:
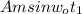 = 0.1 Am
= 0.1 Am
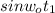 = 0.1
= 0.1
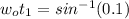
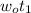 = 5.7392
= 5.7392
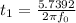
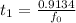
Using sine wave for
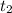 ; we have:
; we have:
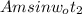 = 0.9 Am
= 0.9 Am
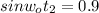
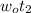 =
=
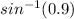
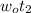 = 64.158
= 64.158
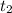 =
=
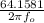
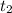 =
=
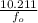
Change in rise time
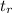 =
=
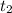 -
-
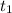
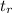 =
=

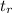 =
=
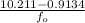
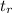 =
=
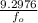
since;
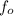 = 50 kHz =
= 50 kHz =
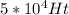
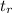 =
=
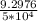
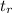 = 1.85952 × 10⁻⁴
= 1.85952 × 10⁻⁴
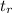 = 185.952 × 10⁻⁶ sec
= 185.952 × 10⁻⁶ sec
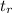 = 185.95 μ sec
= 185.95 μ sec
∴ The rise in time in (μ sec) for the sinosodial signal at 50 kHz = 185.95 μ sec