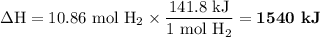Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Gather all the information in one place
Mᵣ: 2.016
H₂ + ½O₂ ⟶ H₂O + 148.1 kJ
m/g: 21.9
2. Moles of H₂
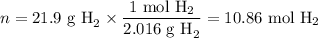
3. Calculate ΔH
Treat the heat AS IF it were a reactant or product. In this case, the reaction is exothermic, so the heat is a product.
In effect, you have 148.1 mol of "kJ"s for each mole of hydrogen and