Answer: The concentration of ethene is 0.286 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate law expression for first order kinetics is given by the equation:
![k=(2.303)/(t)\log([A_o])/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/bbi6c2ny1tf8wlzntta3i570f6pal714ld.png)
where,
k = rate constant =
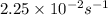
t = time taken for decay process = 15.0 s
![[A_o]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/3jrctnxyrdjmiz9ngr0s6o9r3hdvpo6qhe.png) = initial amount of the reactant = 0.500 M
= initial amount of the reactant = 0.500 M
[A] = amount left after decay process = ?
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![2.25* 10^(-2)s^(-1)=(2.303)/(15.0s)\log(0.500)/([A])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/i9k7uu0zk9zafdsbqlcm1m08v7qugtbtvz.png)
![[A]=0.357M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/zcu2nzn4y4lscn1e6xdqcn3twmuiibw8ge.png)
The concentration of reactant consumed = (0.500 - 0.357) M = 0.143 M
For the given chemical reaction:
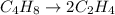
1 mole of butene produces 2 moles of ethene
So, concentration of ethene = (2 × 0.143) M = 0.286 M
Hence, the concentration of ethene is 0.286 M