Answer : The value of equilibrium constant
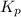 for the reaction is, 3.82
for the reaction is, 3.82
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the pressure of phosgene gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
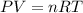
where,
P = Pressure of phosgene gas = ?
V = Volume of phosgene gas = 1.50 L
n = number of moles phosgene =
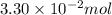
R = Gas constant =
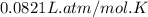
T = Temperature of phosgene gas = 800 K
Putting values in above equation, we get:
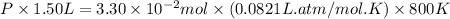
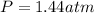
Now we have to calculate the value of equilibrium constant.
The balanced equilibrium reaction is:
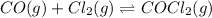
Initial pressure 0 0 1.44
At eqm. P P (1.44-P)
The expression of equilibrium constant
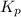 for the reaction will be:
for the reaction will be:
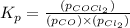
As we are given that:
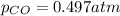
That means, P = 0.497 atm
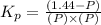
Now put all the values in this expression, we get :
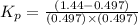
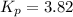
Thus, the value of equilibrium constant
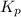 for the reaction is, 3.82
for the reaction is, 3.82