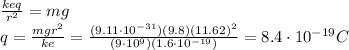Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
The electron remains suspended is the electric force acting on it (upward) is equal in magnitude to the force of gravity (downward) acting on it.
The electric force on the electron is given by:
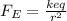
where:
k is the Coulomb's constant
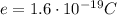 is the magnitude of the electric charge
is the magnitude of the electric charge
q is the unknown positive charge
r = 11.62 m is the distance between the electron and the charge
The force of gravity on the electron is
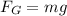
where
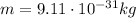 is the mass of the electron
is the mass of the electron
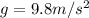 is the acceleration due to gravity
is the acceleration due to gravity
Equating the two forces and solving for q, we find: