Answer:
-35 mV and +56 mV
Step-by-step explanation:
The membrane potential is the energy that is needed to drive membrane changes across the phospholipid bi-layer membrane.
Ions can move in and out of the cell through protein channels. The movement of the ions is as a result of concentration that affect the operation of ion gates.
The reverse potential is given by the Nernst equation:
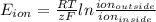
where, R = gas constant
T = temperature (Kelvin)
z = ion charge
F = Faraday's charge
The potential is calculated and the result is -35 mV and +56 mV respectively.