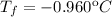Answer:
- 1. Boiling point: 100.264ºC
- 2. Freezing point: - 0.960ºC
Step-by-step explanation:
1. Boling point
The boiling point of a solvent will increase when a solute is added. The boiling point elevation is a colligative property.
When a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte solute is added to a solvent, the increase of the boiling point may be calculated using the formula:
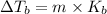
Where m is the molality and Kb is the the molal boiling point constant (for water, Kb = 0.512ºC/m ).
Substitute and compute:
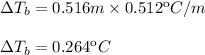
Hence, add the increase in the boiling point to the normal boiling point of water: 100.000ºC
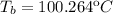
2. Freezing point
The freezing point of a solve will decrease when a solute is added. The depression on the freezing point is another colligative property.
When a nonvolatile, nonelectrolyte solute is added to a solvent, the depression of the boiling point may be calculated using the formula:
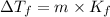
Where m is the molality and Kf is the the molal freezing point constant (for water, Kf = 1.86 ºC/m ).
Substitute and compute:
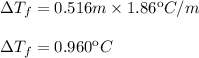
Subtract the decrease on the freezing point from the normal freezing point of water: 0.000ºC