Answer:
R=100 Ohm, V=11.97 volts and I=0.12 amperes
R=10 Ohm, V=10.25 volts and I=1.20 amperes
R=2 Ohm, V=6.26 volts
Step-by-step explanation:
The potential difference (voltage) of a battery with internal resistance is:
 (1)
(1)
with
 the electromotive force (the voltage the batteries say to has) , I the current and r the internal resistance. By Ohm's law the current that passes through the resistor is:
the electromotive force (the voltage the batteries say to has) , I the current and r the internal resistance. By Ohm's law the current that passes through the resistor is:
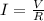 (2)
(2)
using (2) on (1):

solving for V:

 (3)
(3)
R=100 Ohm

R=10 Ohm

R=2 Ohm

Because we have now the values of I on the circuit (is the same through all the components because is a series circuit)
We use back substitution on (1) to find the current:
R=100 Ohm

R=10 Ohm
