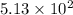Answer: The value of
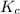 for
for
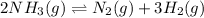 reaction is
reaction is
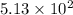
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Initial moles of nitrogen gas = 1.30 moles
Initial moles of hydrogen gas = 1.65 moles
Equilibrium moles of ammonia = 0.100 moles
Volume of the container = 1.00 L
For the given chemical equation:
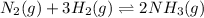
Initial: 1.30 1.65
At eqllm: 1.30-x 1.65-3x 2x
Evaluating the value of 'x'
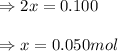
The expression of
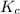 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([NH_3]^2)/([N_2]* [H_2]^3)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/stuooext8cmnemexxxycp5olzi0dwhr7bq.png)
Equilibrium moles of nitrogen gas =
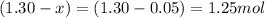
Equilibrium moles of hydrogen gas =
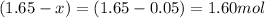
Putting values in above expression, we get:
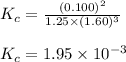
Calculating the
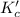 for the given chemical equation:
for the given chemical equation:
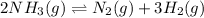
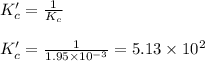
Hence, the value of
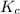 for
for
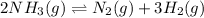 reaction is
reaction is