Answer:
0.224 m
Step-by-step explanation:
The motion of the first 20 ms is a uniformly accelerated motion. With an initial velocity of 0 m/s, the equation of motion used is
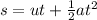
where
 is the distance,
is the distance,
 is the initial velocity,
is the initial velocity,
 is the acceleration and
is the acceleration and
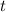 is the time.
is the time.
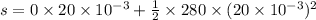
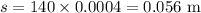
The velocity,
 , at the end of this part of the motion is
, at the end of this part of the motion is
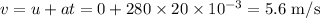 .
.
This velocity is maintained for 30 ms through a distance of
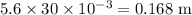
The total distance is 0.056 + 0.168 = 0.224 m