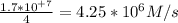Answer:
How would the rate of disappearance of ethyl bromide change if the solution were diluted by adding an equal volume of pure ethyl alcohol to the solution?
If the solution were diluted by adding an equal volume of pure ethyl alcohol to the solution, then thee rate of reaction will decrease by a factor of 4 to 4.25×10⁶ M/s
Step-by-step explanation:
For a first order reaction we have
Rate =
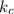 [A] where [A] is the concentration of the reagent
[A] where [A] is the concentration of the reagent
Hence the reaction between (C₂H₅Br) and OH⁻ is given by
Rate = Kc[C₂H₅Br][OH⁻]
The addition of pure ethyl which only dilute the concentration of the reactants we have
Final concentration = (initial concentration)/ 2
Therefore the rate becomes
Rate =
![k_(c) ([C_(2) H_(5) Br])/(2) ([OH^(-) ])/(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/high-school/fpcae0nqdhhk61huoeipbi5l23yw6l13mv.png) =
=
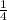 ×Kc[C₂H₅Br][OH⁻]
×Kc[C₂H₅Br][OH⁻]
Then the rate of reaction is divided by 4 thus
The rate of the reaction =