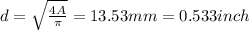Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Initially, we should analyse the system- load and wire are connected in series, which means that they have the same current flow, but we have a voltage drop across the wire.
As it is given, wire is made from aluminum with the specific resistance of 2.82 Ohm*m.
As the specific resistance is given in SI units, we can convert distance in the meters to make calculations easier:
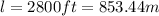
As, the maximum loss of the voltage is 3% and the operating voltage is 480V, we can calculate the maximum allowed drop across the wires:
Vloss=480*3%=14.4 V
Using Ohm's law, we can calculate the maximum allowed resistance of the wire for the given current:
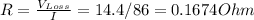
Resistance of the wire, can be calculated using its specific resistance D, length l and area A:
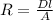
From this equation, we can calculate minimal required area of the wire:
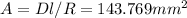
From where, assuming, that the wire has circular cross section, we can find its diameter: