Answer : The partial pressure of B in the container is, 25.94 atm
Explanation : Given,
Total pressure = 38.9 atm
The given chemical reaction is:
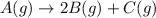
Initial pressure p 0 0
At eqm. 0 2p p
The total pressure expression will be:
Total pressure = 2p + p
38.9 atm = 2p + p
38.9 atm = 3p
p = 12.97 atm
Now we have to calculate the partial pressure of B in the container.
The partial pressure of B in the container = 2p = 2(12.97) = 25.94 atm
Thus, the partial pressure of B in the container is, 25.94 atm