Answer: The vapor pressure of the solution is 43.55 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the number of moles, we use the equation:
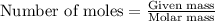 .....(1)
.....(1)
Given mass of water = 35.0 g
Molar mass of water = 18 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
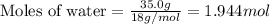
Given mass of ethyl alcohol = 100.0 g
Molar mass of ethyl alcohol = 46 g/mol
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
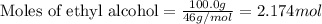
Total moles of solution = [1.944 = 2.174] moles = 4.118 moles
- Mole fraction of a substance is given by:
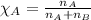
For water:
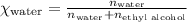
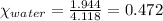
For ethyl alcohol:
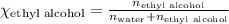
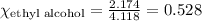
Dalton's law of partial pressure states that the total pressure of the system is equal to the sum of partial pressure of each component present in it.
To calculate the vapor pressure of the solution, we use the law given by Dalton, which is:
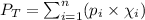
Or,
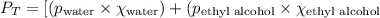
We are given:
Vapor pressure of water = 23.8 mmHg
Vapor pressure of ethyl alcohol = 61.2 mmHg
Putting values in above equation, we get:
![p_T=[(23.8* 0.472)+(61.2* 0.528)]\\\\p_T=43.55mmHg](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4qvf2slvsf75w0hyn8jtdbqh1cvnkczta5.png)
Hence, the vapor pressure of the solution is 43.55 mmHg