Answer:
- You must add 1.000 liters of pure water to the 1.000 liters of solution, to dilute the molarity by a factor of two.
Step-by-step explanation:
To reduce the molarity by a fraction of two you need to duplicate the volume of the solution.
Molarity is defined as the number of moles of solute per liter of solution. Hence, if you want to dilute, i.e. to reduce the concentration, by a factor of two, given that you have the number of moles of solute constant, you need to add water to duplicate the volume of the solution.
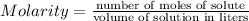
Mathematically, in the formula above you want to reduce the quotient by a factor of two, while the numerator does not change. Then, you need to multiply the denominator by two.
Thus, you must add 1.000 liters of pure water to the 1.000 liters of solution, to dilute the molarity by a factor of two.