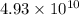Answer : The rate constant of the reaction is increased by factor,
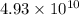
Solution :
According to the Arrhenius equation,
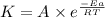
The expression used with catalyst and without catalyst is,
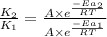
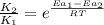
where,
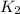 = rate of reaction with catalyst
= rate of reaction with catalyst
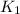 = rate of reaction without catalyst
= rate of reaction without catalyst
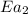 = activation energy with catalyst = 23.0 kJ/mol = 23000 J/mol
= activation energy with catalyst = 23.0 kJ/mol = 23000 J/mol
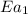 = activation energy without catalyst = 84.0 kJ/mol = 84000 J/mol
= activation energy without catalyst = 84.0 kJ/mol = 84000 J/mol
R = gas constant = 8.314 J/mol.K
T = temperature =
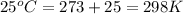
Now put all the given values in this formula, we get
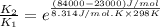
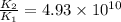
Therefore, the rate constant of the reaction is increased by factor,