If two vectors have different magnitudes and opposite directions the sum of both the vectors will be a non-zero component.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let us assume that both the vectors lie in x-axis with the magnitudes of
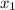 and
and
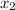 . If the sum of the vectors are zero, i.e if
. If the sum of the vectors are zero, i.e if
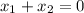 then,
then,
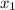 will be equal to
will be equal to
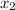 which generally states that the vectors are of same magnitude.
which generally states that the vectors are of same magnitude.
So, from this we can come to a conclusion that the sum of two vectors with different magnitudes and opposite directions will not be zero.
Additional information: In contrast to the sum, the dot-product of two vectors have different magnitudes and opposite directions will be zero.