Answer : The heat absorbed by the gas is closest to 34.9 kJ
Explanation :
First we have to calculate the moles of gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
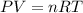
where,
P = Pressure of gas = 70 kPa = 70000 Pa
V = Volume of gas =
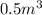
n = number of moles = ?
R = Gas constant =
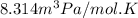
T = Temperature of gas =
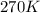
Putting values in above equation, we get:
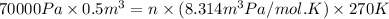
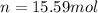
Heat released at constant volume is known as internal energy.
The formula used for change in internal energy of the gas is:
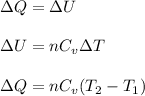
where,
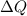 = heat at constant volume = ?
= heat at constant volume = ?
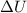 = change in internal energy
= change in internal energy
n = number of moles of gas = 15.59 moles
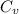 = heat capacity at constant volume gas = 28.0 J/mol.K
= heat capacity at constant volume gas = 28.0 J/mol.K
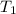 = initial temperature = 350 K
= initial temperature = 350 K
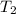 = final temperature = 270 K
= final temperature = 270 K
Now put all the given values in the above formula, we get:
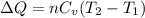
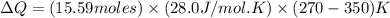
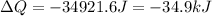
Thus, the heat absorbed by the gas is closest to 34.9 kJ