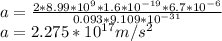Answer:
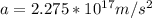
Step-by-step explanation:
The electron is negatively charged .The magnitude of force acting on on electron is
F=|e| E
Where E is electric field of long non conducting rod E=1/2πε₀r with linear charge density λ=6.7μC/m
From Newtons second laws
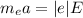
the initial acceleration of electron is given by:
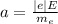
a=(|e|λ) /2πε₀rm= 2(|e|λ) / 4πε₀rm
Where 2 is multiplied on both numerator and denominator to simplify calculation
The electron is initially at distance r=9.3cm=0.093 m from rod
So