Answer:
Resultant amplitude is 0.53 m.
Step-by-step explanation:
Amplitude is defined as the maximum displacement of wave particles from their respective mean positions.
The resulting amplitude of any two waves is given by the relation :
A =
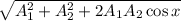
Here, A is resultant amplitude, A₁ and A₂ are the amplitudes of two waves respectively and x is the difference in phase angle of the two waves.
According to the problem, A₁ is 0.4 m , A₂ is 0.23 m and x is zero. So, the above equation becomes,
A =

A =
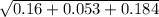
A = 0.63 m