Answer: The total heat required for the conversion process is 1228.5 J
Step-by-step explanation:
The processes involved in the given problem are:
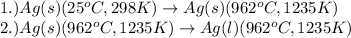
To calculate the amount of heat absorbed, we use the equation:
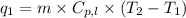
where,
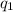 = amount of heat absorbed = ?
= amount of heat absorbed = ?
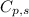 = specific heat capacity = 0.235 J/g.K
= specific heat capacity = 0.235 J/g.K
m = mass of silver = 9.70 g
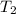 = final temperature = 1235 K
= final temperature = 1235 K
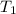 = initial temperature = 298 K
= initial temperature = 298 K
Putting all the values in above equation, we get:
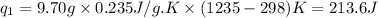
To calculate the amount of heat released, we use the equation:
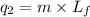
where,
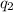 = amount of heat absorbed = ?
= amount of heat absorbed = ?
m = mass of silver = 9.70 g
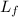 = latent heat of fusion = 11.3 kJ/mol =
= latent heat of fusion = 11.3 kJ/mol =
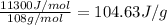 (Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J; Molar mass of silver = 108 g/mol)
(Conversion factor: 1 kJ = 1000 J; Molar mass of silver = 108 g/mol)
Putting all the values in above equation, we get:
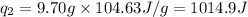
Total heat required for the conversion =
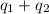
Total heat required for the conversion =
![[213.6+1014.9]J=1228.5J](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/u5uwoh9w4bap0aarrlvxqi55a04owhj3ux.png)
Hence, the total heat required for the conversion process is 1228.5 J