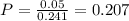Answer:
a) 0.336
b) 0.207
Explanation:
A probability is the number of desired outcomes divided by the number of total outcomes.
We solve this problem building the Venn's diagram of these probabilities.
I am going to say that:
A is the probability that a person from the clinical population is diagnosed with mental disorder.
B is the probability that a person from the clinical population is diagnosed with alcohol related disorder.
We have that:
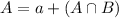
In which a is the probability that a person is diagnosed with mental disorder but not alcohol related disorder and
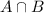 is the probability that a person is diagnosed with both of these disorders.
is the probability that a person is diagnosed with both of these disorders.
By the same logic, we have that:
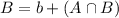
We find the values of a,b and the intersection, starting from the intersection.
5% are diagnosed with both disorders.
This means that
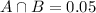
14.9% are diagnosed with an alcohol-related disorder
This means that
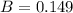
So
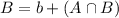
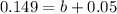
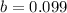
24.1% are diagnosed with a mental disorder
This means that
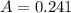
So
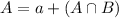
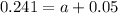
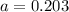
(a) What is the probability that someone from the clinical population is diagnosed with a mental disorder, knowing that the person is diagnosed with an alcohol-related disorder?
Desired outcomes:
Mental and alcohol-related disorders, which
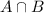 . So
. So
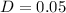
Total outcomes:
Alcohol-related disorder, which is B. So
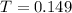
Probability:
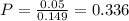
(b) What is the probability that someone from the clinical population is diagnosed with an alcohol-related disorder, knowing that the person is diagnosed with a mental disorder?
Desired outcomes:
Mental and alcohol-related disorders, which
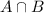 . So
. So
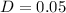
Total outcomes:
Mental disorder, which is B. So
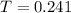
Probability: