Answer: The molar mass of the sample is 120.6 g/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the depression in freezing point, we use the equation:
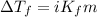
Or,
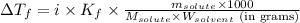
where,
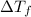 = depression in freezing point = 0.42°C
= depression in freezing point = 0.42°C
i = Vant hoff factor = 1 (For non-electrolytes)
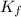 = molal freezing point elevation constant = 5.065°C/m
= molal freezing point elevation constant = 5.065°C/m
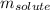 = Given mass of solute (sample) = 0.500 g
= Given mass of solute (sample) = 0.500 g
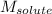 = Molar mass of solute (sample) = ? g/mol
= Molar mass of solute (sample) = ? g/mol
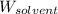 = Mass of solvent (benzene) = 50.0 g
= Mass of solvent (benzene) = 50.0 g
Putting values in above equation, we get:
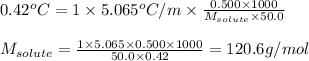
Hence, the molar mass of the sample is 120.6 g/mol