Answer:
a) F test is a statistical test that uses a F Statistic to compare two population variances, with the sample deviations s1 and s2. The F statistic is always positive number since the variance it's always higher than 0. The statistic is given by:
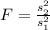
b) H0:
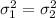
H1:
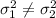
c)
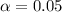 represent the significance level provided
represent the significance level provided
Confidence =0.95 or 95%
d) We need to calculate the degrees of freedom first. For the numerator we have
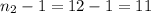 and for the denominator we have
and for the denominator we have
We can find the critical value on the F table or with the following excel code: "=F.INV(1-0.025,11,11)"
And we got
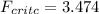
e)
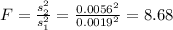
f) Since our calculated value 8.68 is higher than the critical value of 3.474 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis and at 5 % of significance we can conclude that the two variances are different.
Explanation:
Data given and notation
We can calculate the mean and deviation with the following formulas:
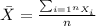
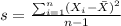
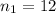 represent the sampe size for the new drill
represent the sampe size for the new drill
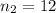 represent the sample size for the old drill
represent the sample size for the old drill
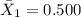 represent the sample mean for the new drill
represent the sample mean for the new drill
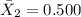 represent the sample mean for the old drill
represent the sample mean for the old drill
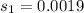 represent the sample deviation for the new drill
represent the sample deviation for the new drill
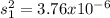 represent the sample variance for the new drill
represent the sample variance for the new drill
represent the sample deviation for the old drill
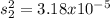 represent the sample variance for the old drill
represent the sample variance for the old drill
Part a
F test is a statistical test that uses a F Statistic to compare two population variances, with the sample deviations s1 and s2. The F statistic is always positive number since the variance it's always higher than 0. The statistic is given by:
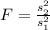
Solution to the problem
Part B: System of hypothesis
We want to test if the variation for oil stocks it's higher than the variation for utility stocks, so the system of hypothesis are:
H0:
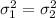
H1:
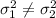
Part c: Significance level
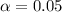 represent the significance level provided
represent the significance level provided
Confidence =0.95 or 95%
Part D: Critical value
We need to calculate the degrees of freedom first. For the numerator we have
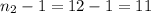 and for the denominator we have
and for the denominator we have
We can find the critical value on the F table or with the following excel code: "=F.INV(1-0.025,11,11)"
And we got
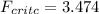
Part E :Calculate the statistic
Now we can calculate the statistic like this:
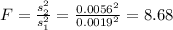
Part F: Decision
Since our calculated value 8.68 is higher than the critical value of 3.474 we have enough evidence to reject the null hypothesis and at 5 % of significance we can conclude that the two variances are different.