Answer: The value of
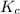 for the given reaction is 1.435
for the given reaction is 1.435
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
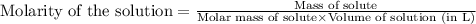
Given mass of
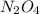 = 9.2 g
= 9.2 g
Molar mass of
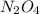 = 92 g/mol
= 92 g/mol
Volume of solution = 0.50 L
Putting values in above equation, we get:
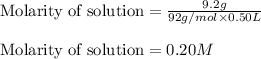
For the given chemical equation:
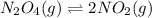
Initial: 0.20
At eqllm: 0.20-x 2x
We are given:
Equilibrium concentration of
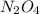 = 0.057
= 0.057
Evaluating the value of 'x'
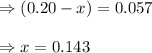
The expression of
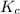 for above equation follows:
for above equation follows:
![K_c=([NO_2]^2)/([N_2O_4])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/vkb4qh8uu2trux626hsyhcrfq5sgbbyvg6.png)
![[NO_2]_(eq)=2x=(2* 0.143)=0.286M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nhdyu3pypjp2yekwxtk272gzdja1rgnbe1.png)
![[N_2O_4]_(eq)=0.057M](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/e4n7td0or5jvr9hnto8q6ajiocy604bgrh.png)
Putting values in above expression, we get:
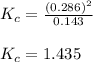
Hence, the value of
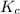 for the given reaction is 1.435
for the given reaction is 1.435