Answer:
Acceleration=
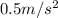
Speed=0.67 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given that
Horizontal force=F=20 N
Mass of box=m=40 kg
We know that
Acceleration=
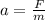
Using the formula
Acceleration of box=
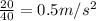
The acceleration of the box=
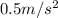
Initial velocity=u=0
Force=F=30 N
Distance=s=0.3 m
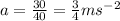
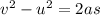
Substitute the values
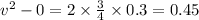
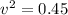
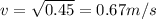
Hence, the speed of the box after it has been pulled a distance of 0.3 m=0.67 m/s