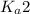Answer: To calculate the pH of the buffer composed of
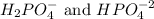 , we use the
, we use the
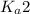
Step-by-step explanation:
Phosphoric acid is a triprotic acid and it will undergo three dissociation reaction each having their respective dissociation constants.
The chemical equation for the first dissociation reaction follows:
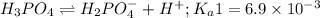
The chemical equation for the second dissociation reaction follows:
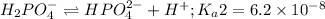
The chemical equation for the third dissociation reaction follows:
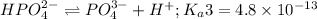
To form a buffer composed of
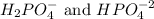 , we use the
, we use the
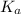 of second dissociation process
of second dissociation process
To calculate the
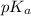 , we use the equation:
, we use the equation:
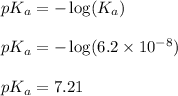
To calculate the pH of buffer, we use the equation given by Henderson Hasselbalch:
![pH=pK_a2+\log(\frac{[\text{conjugate base}]}{[\text{weak acid}]})](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5o9rdly1cxn23qktqk0jbklryew9ob79t5.png)
![pH=pK_a2+\log(([HPO_4^(2-)])/([H_2PO_4^-]))](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/k1s18jpblpxncpvay9a0yl7ui7qmaeangm.png)
We are given:
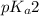 = negative logarithm of second acid dissociation constant of phosphoric acid = 7.21
= negative logarithm of second acid dissociation constant of phosphoric acid = 7.21
![[HPO_4^(2-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/izpqikem7rxpk5e4wi16v8q8hxphxuawa8.png) = concentration of conjugate base
= concentration of conjugate base
![[H_2PO_4^(-)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/nwng5uvm6tesi6pfrj4adu73d70rfebrpz.png) = concentration of weak acid
= concentration of weak acid
Hence, to calculate the pH of the buffer composed of
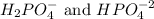 , we use the
, we use the